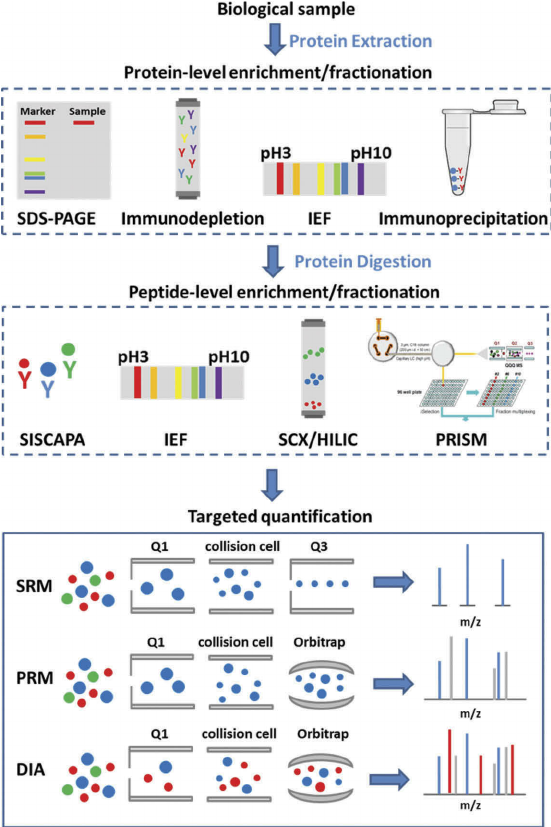
Introduction
Biological and chemical samples, meticulously collected, form the basis for groundbreaking discoveries in scientific research. However, the process of transforming a raw sample into meaningful data for researchers across diverse fields is well-defined and intricate. This blog post details the critical steps involved in this process.
1. Scrupulous Sample Acquisition
The first step is the scrupulous acquisition of the sample. This ensures the sample accurately represents the target population or system being studied. Depending on the sample type (tissue, blood, soil, water), this may involve aseptic techniques for biological samples or specialized collection tools for environmental samples. Rigorous protocols are essential to minimize contamination and preserve the sample's inherent properties.
2. Sample Processing and Preservation
Following acquisition, samples often undergo a series of processing steps to prepare them for further analysis. These steps, like homogenization (biological) or filtration (chemical), achieve homogeneity within the sample. Preservation methods, such as cryopreservation or specific buffer addition, stabilize the sample's biochemical composition and prevent degradation.
3. Sample Fractionation and Enrichment
For complex samples containing numerous biomolecules or chemical components, fractionation techniques may be implemented. These techniques, such as chromatography or centrifugation, separate the sample into distinct fractions. Each fraction may be enriched with specific analytes of interest. This targeted enrichment improves the sensitivity and accuracy of subsequent analyses.
4. Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis
The culmination of the process is the analysis of the sample using various techniques. Quantitative analysis methods, like spectrophotometry or mass spectrometry, allow researchers to measure the exact concentration of specific analytes within the sample. Conversely, qualitative techniques, such as gel electrophoresis or immunoassays, provide information on the presence or absence of specific molecules.
5. Data Acquisition and Interpretation
The data generated from the chosen analytical technique(s) is meticulously acquired and documented. Depending on the complexity of the data, researchers may employ advanced computational tools and statistical analyses to extract meaningful patterns and trends. By meticulously interpreting the data in the context of the experimental design and relevant scientific literature, researchers can formulate robust conclusions and advance scientific knowledge.
Conclusion
The successful transformation of a raw biological or chemical sample into interpretable data relies on a rigorously defined process. From the initial acquisition to the final analysis, each step plays a vital role in ensuring the integrity and reliability of the data obtained. By adhering to these rigorous protocols, researchers can embark on the path to groundbreaking discoveries fueled by the power of meticulously collected and analyzed samples.