The One Health concept emphasizes the interconnectedness of animal, human, and environmental health. Veterinary science plays a critical role in this approach by applying its expertise in animal health to benefit public health and promote ecosystem wellbeing.
Zoonotic Disease Surveillance and Control
Veterinarians are on the front line for identifying and tracking zoonotic diseases - illnesses that can jump between animals and humans. They play a vital role in:
- Early detection: Veterinarians in clinical practice, public health, and research actively monitor animal populations for zoonotic disease outbreaks. This allows for early intervention and outbreak management strategies.
- Investigating outbreaks: Veterinary epidemiologists work with public health officials to trace the source of zoonotic outbreaks, understand how they spread, and implement control measures.
- Vaccine development and use: Veterinary science significantly contributes to developing and applying vaccines for zoonotic diseases, protecting both animal and human populations.
For example, veterinary surveillance led to the identification of Nipah virus in pigs, a zoonotic pathogen with significant human health consequences. Similarly, veterinary research has been instrumental in developing rabies vaccines, leading to a substantial reduction in the global disease burden.
Food Safety and Security
Veterinarians safeguard the food chain by ensuring the health of food animals. This includes:
- Disease prevention and control: Veterinary interventions like vaccination programs and biosecurity measures minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses in animals, preventing their transmission to humans through contaminated food products.
- Antimicrobial resistance control: Veterinarians play a crucial role in promoting the responsible use of antibiotics in animals, thereby curbing the emergence of antimicrobial resistance – a significant public health threat.
- Food inspection and safety regulations: Veterinarians working in food inspection ensure that animal-derived food products are safe for human consumption by adhering to established hygiene and safety protocols.
The emergence of zoonotic pathogens like E. coli and Salmonella highlights the importance of veterinary involvement in food safety.
Environmental Health
Veterinarians contribute to environmental health by:
- Wildlife Disease Management: Diseases in wildlife can spread to domestic animals and humans. Veterinarians play a critical role in wildlife disease surveillance, outbreak response, and conservation efforts to maintain healthy ecosystems.
- Parasite Control: Parasitic infections can affect both animals and humans. Veterinarians contribute to developing and implementing parasite control programs, safeguarding public and animal health.
- Antimicrobial Resistance in the Environment: Veterinary expertise is essential in understanding how antimicrobial resistance spreads in the environment and developing strategies to mitigate it.
For instance, research by veterinary epidemiologists has been instrumental in understanding how West Nile Virus, a mosquito-borne zoonotic disease, spreads, with significant implications for environmental and public health.
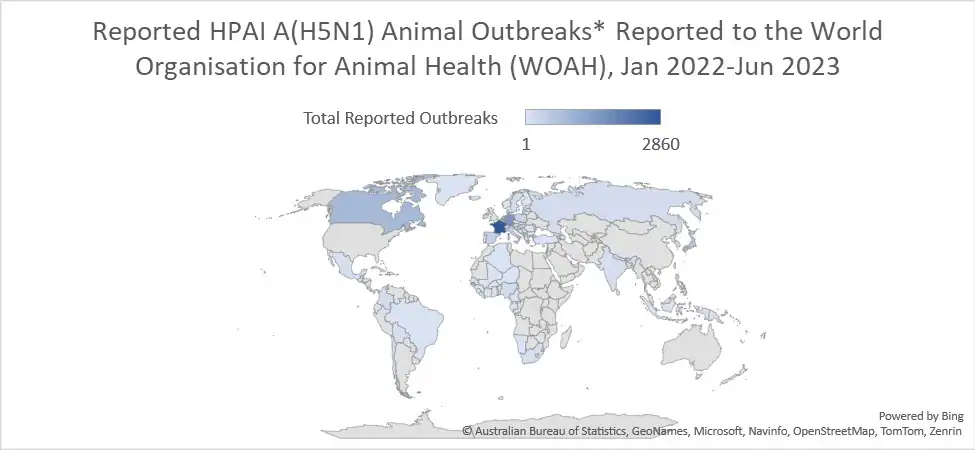
Ensuring Early Detection of Avian Influenza
Avian influenza, particularly the H5N1 strain, is a significant zoonotic threat. Early detection of outbreaks in poultry populations is critical to prevent its spread to humans and other animals. Maxanim, a company within the Gentaur Group, offers the Avian Influenza Virus H5N1 Real Time RT-PCR Kit, a reliable diagnostic tool specifically designed for the rapid and accurate detection of Avian Influenza Virus H5N1. This kit can be a valuable asset for veterinarians and public health officials working to safeguard animal and human health by enabling swift diagnosis and outbreak control measures.
Additionally, for those interested in exploring the Maxanim Avian Influenza Virus H5N1 Real Time RT-PCR Kit in more detail, information can be found on the website.
Conclusion
Veterinary science is a fundamental part of the One Health approach. By collaborating with human health professionals and environmental scientists, veterinarians play a vital role in protecting animal, human, and environmental health, fostering a more resilient and healthy world for all.
Learn more about the One Health concept in this video.