This article explores the essential functions of molecular chaperones in maintaining protein homeostasis within cells.
Protein Homeostasis
Protein homeostasis, or proteostasis, is a critical cellular process ensuring proteins fold correctly, assemble properly, and function as intended. Misfolded or aggregated proteins can disrupt cellular function and potentially lead to disease.
Molecular Chaperones
Molecular chaperones are a diverse group of proteins that play a vital role in protein homeostasis. They assist with several processes:
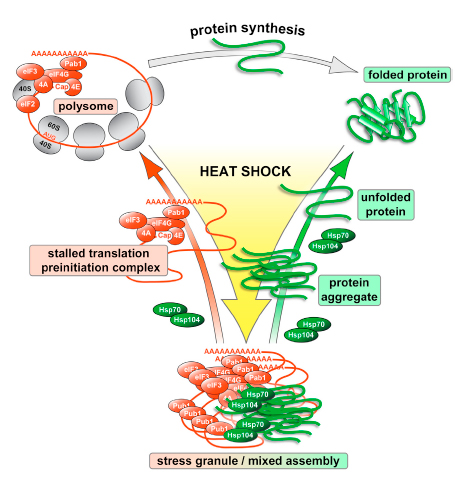
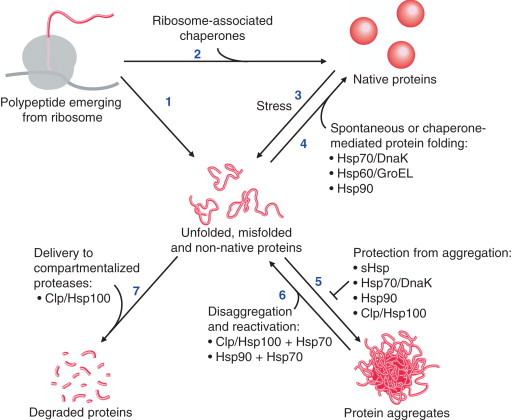
- Folding assistance: Newly synthesized protein chains are prone to misfolding. Chaperones bind to these chains, preventing incorrect interactions and guiding them towards their proper folded state.
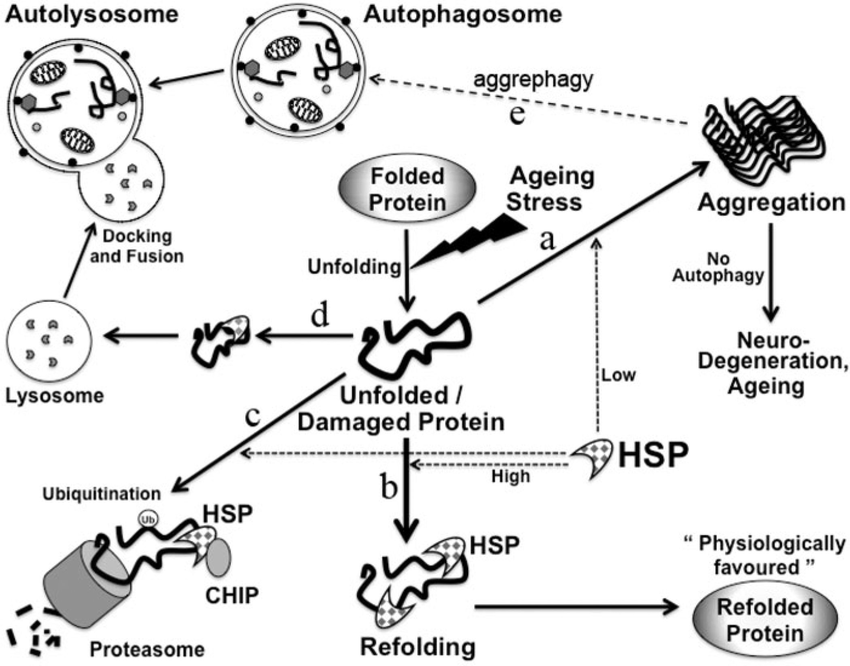
- Refolding: Even correctly folded proteins can misfold under stress conditions. Chaperones can recognize and refold these denatured proteins, preventing aggregation.
- Preventing aggregation: Misfolded proteins have a high tendency to clump together, forming harmful inclusions. Chaperones can encapsulate unfolding proteins, shielding them from inappropriate interactions and promoting proper folding.
- Disaggregation: Despite chaperone activity, some proteins may still aggregate. Certain chaperones can disassemble these protein aggregates, allowing for refolding or targeting for degradation.
- Targeting for degradation: When refolding or disaggregation fails, irreversibly misfolded proteins must be eliminated. Chaperones can interact with cellular machinery to mark these proteins for degradation by the proteasome.
Importance of Protein Homeostasis
Disruptions in protein homeostasis, often caused by mutations in chaperone genes or increased cellular stress, are linked to various neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Understanding chaperone function provides valuable insights into these diseases and potential therapeutic strategies.
Research and Resources
Researchers studying protein folding and misfolding rely on high-quality tools. Companies like Maxanim offer a comprehensive selection of molecular chaperones, purified proteins, and antibodies to support chaperone research.

Conclusion
Molecular chaperones are essential for maintaining protein homeostasis within cells. They play a critical role in ensuring proteins fold correctly, avoid aggregation, and function as intended. Further research on the specific functions of different chaperone families holds promise for developing novel therapeutics to combat protein misfolding diseases.
Learn more about Protein Folding and Chaperones in the following video.