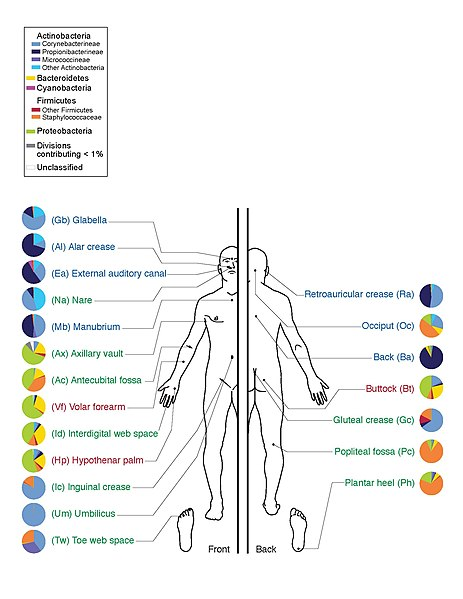
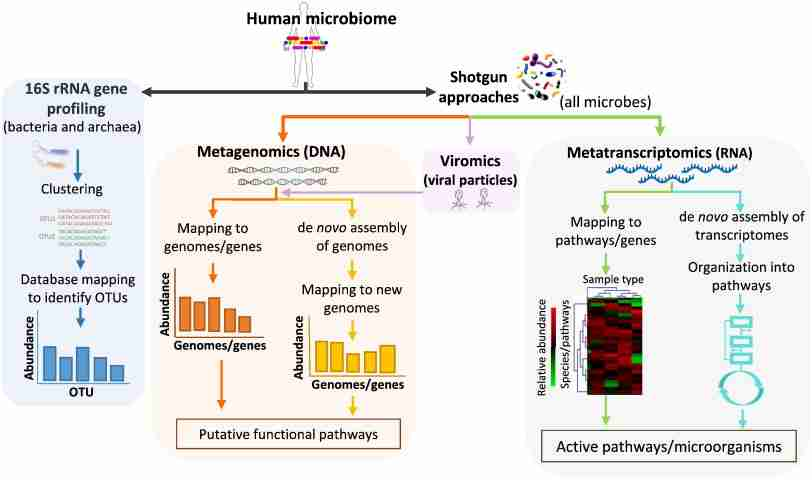
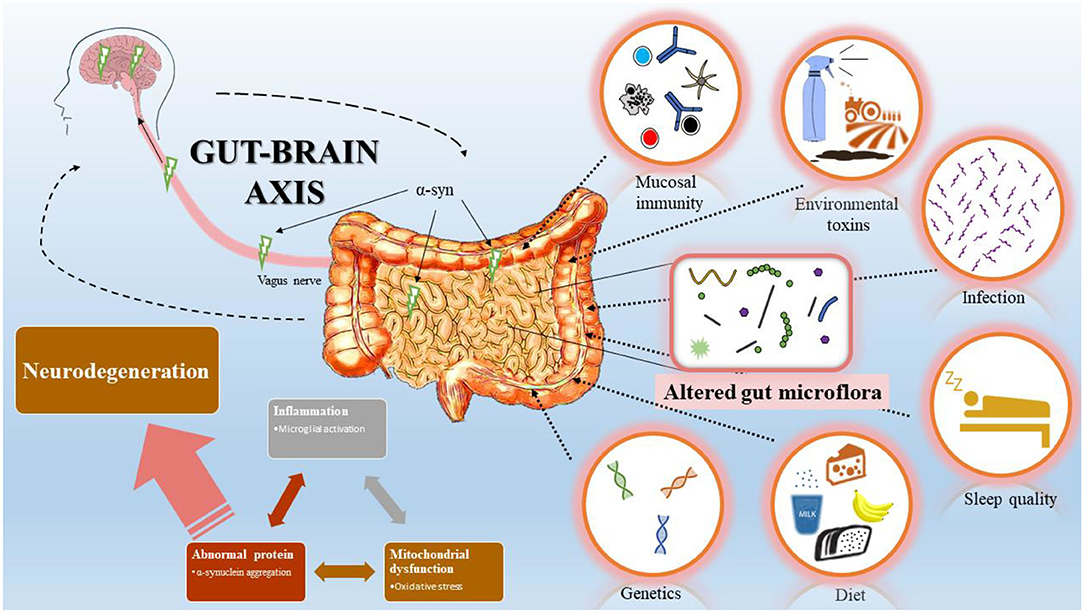
The microbiome, the community of microorganisms living within a human or other animal, has become a major area of scientific study. These microbes play a critical role in health, affecting metabolism, immunity, and even brain function. Researchers use various laboratory techniques to analyze the microbiome and understand its impact. This blog post will explore some key techniques and current research trends in microbiome science.
Techniques for Microbiome Analysis:
- 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing: This technique targets a specific gene (16S ribosomal RNA) to identify the types of bacteria present in a sample. By amplifying and sequencing this gene, scientists can determine the relative abundance of different bacterial species in the microbiome.
- Metagenomics: This approach involves sequencing all the DNA extracted from a sample, providing a more detailed picture of the microbiome. It can reveal not only bacteria but also archaea, fungi, and viruses present. Metagenomics allows researchers to identify the genes and metabolic pathways encoded by the microbial community.
- Metatranscriptomics: This technique analyzes the messenger RNA (mRNA) isolated from a sample. By looking at the active mRNA, scientists can determine which genes are being expressed by the microbiome and gain insights into the functional processes happening at a specific time.
- Culturing Techniques: While DNA sequencing is powerful, culturing microbes in the lab is still important for functional studies. Researchers use various culture media and conditions to isolate and study specific bacterial strains from the microbiome.
Current Research Trends:
- Microbiome-gut-brain axis: Scientists are investigating the communication between the gut microbiome, the nervous system in the intestines (enteric nervous system), and the brain. This research explores how gut microbes might influence brain development, behavior, and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Personalized medicine: The unique composition of an individual's microbiome may affect how they respond to medications and treatments. Researchers are investigating the potential to use information about the microbiome to develop personalized diagnostics and treatment strategies.
- Engineering the microbiome: Fecal microbiota transplants (FMT) and probiotics are examples of methods to change the composition of the microbiome for health benefits. Research is ongoing to develop safe and effective methods for microbiome modulation.
Conclusion:
Microbiome research is a rapidly developing field with significant implications for human health. As our understanding of the microbiome deepens, we can expect further advancements in diagnostics, personalized medicine, and the development of new therapeutic approaches.
Explore microbiome analysis further in this video: