Chronic illnesses, by definition, are long-lasting conditions that require ongoing medical attention. Navigating the complexities of a chronic illness often involves frequent laboratory testing. These tests, encompassing blood work, urine analysis, and more, provide valuable data points that physicians utilize to diagnose, monitor, and manage a patient's condition.
Diagnostic Power of Lab Tests:
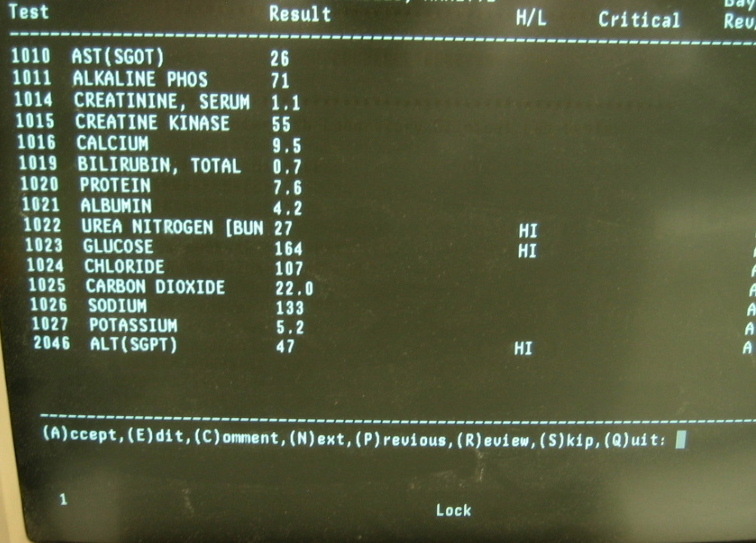
Laboratory tests offer a window into the body's internal workings, revealing physiological and biochemical changes associated with chronic illnesses. Here's a closer look at their diagnostic prowess:
Identifying Biomarkers: Chronic illnesses often leave distinct footprints in the form of biological markers. For instance, elevated blood sugar levels can be indicative of diabetes, while abnormal thyroid hormone levels might suggest thyroid dysfunction.
Assessing Organ Function: Several lab tests evaluate organ health. Liver function tests measure enzymes produced by the liver, providing insights into potential liver damage. Similarly, kidney function tests assess the kidneys' ability to filter waste products from the blood.
Monitoring Disease Progression: Once a chronic illness is diagnosed, lab tests become crucial tools for monitoring its progression. Regularly tracking specific markers allows physicians to gauge treatment efficacy and identify potential complications early on.
Beyond Diagnosis: Treatment Tailoring
Lab results extend their utility beyond diagnosis. They play a vital role in tailoring treatment plans for chronic illnesses:
Optimizing Medication Dosing: Certain medications used to manage chronic conditions, like blood thinners or thyroid replacement hormones, require precise dosing based on individual lab values.
Identifying Medication Side Effects: Lab tests can help uncover potential side effects associated with medications used for chronic illnesses. For instance, monitoring liver enzymes becomes crucial when administering medications that can potentially impact the liver.
Guiding Treatment Adjustments: As a patient's condition evolves or their response to treatment changes, lab results provide crucial insights for adjusting treatment strategies.
In Conclusion:
Laboratory tests are instrumental in the management of chronic illnesses. From aiding in diagnosis and monitoring disease progression to optimizing treatment plans and identifying medication side effects, these tests empower physicians to deliver personalized and evidence-based care. As scientific understanding of chronic illnesses continues to progress, the role of laboratory testing is certain to become even more nuanced and indispensable.