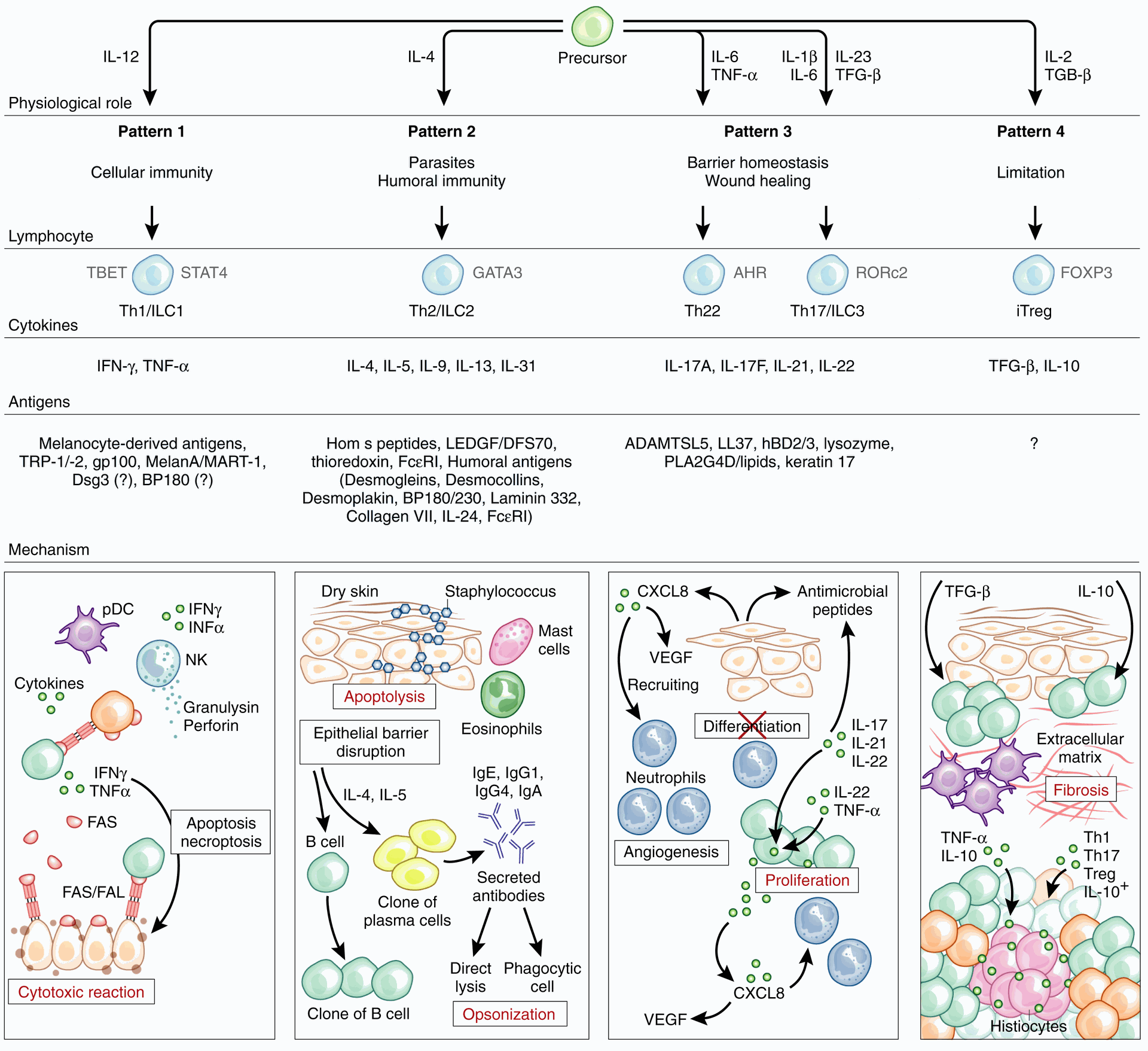
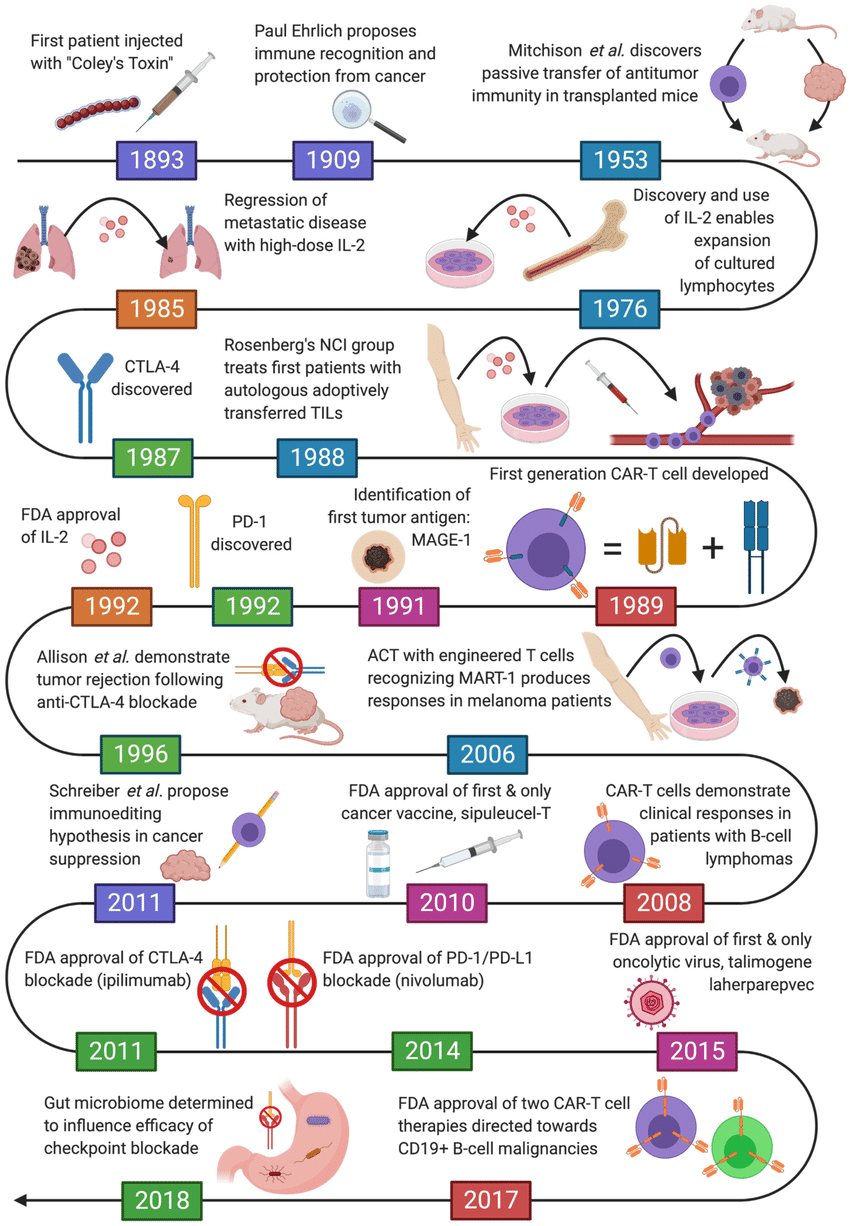
Autoimmune diseases are a group of conditions where the immune system attacks healthy tissues. Traditional treatments often broadly suppress the immune system, increasing the risk of infections. Immunotherapy offers a more specific approach by aiming to modulate the immune response to target the disease process and potentially achieve long-term control.
New Directions in Immunotherapy for Autoimmune Diseases
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors: These drugs, successful in cancer treatment, target pathways that normally regulate T cell activity. Blocking these checkpoints (like CTLA-4 and PD-1) can activate the immune system to target autoreactive cells, but careful monitoring is needed due to potential side effects.
- B-cell depletion: B cells produce antibodies, and some autoimmune diseases involve harmful autoantibodies. Rituximab, an anti-CD20 antibody, effectively depletes B cells in rheumatoid arthritis and other conditions. Research is ongoing to develop more specific methods to target B cells.
- CAR T-cell therapy: This revolutionary cancer treatment shows promise for autoimmune diseases. Engineered T cells expressing CARs specific for autoreactive cells are being investigated for conditions like lupus.
- Targeting the gut microbiome: The gut microbiome significantly impacts immune function. Studies suggest that manipulating the gut bacteria composition might offer a new strategy to regulate immune responses in autoimmune diseases. Companies like Maxanim, a supplier of research reagents, are supporting ongoing investigations into the link between the gut microbiome and autoimmune pathogenesis. This research holds promise for the development of innovative therapies.
Progress and Challenges
Immunotherapy has shown significant benefits in specific autoimmune diseases. TNF-alpha inhibitors like etanercept have revolutionized rheumatoid arthritis treatment, significantly improving patient outcomes. However, challenges remain:
- Specificity: Finding the right balance between targeting the harmful immune response and avoiding excessive immune suppression is crucial.
- Heterogeneity: Autoimmune diseases are highly variable, requiring personalized treatment approaches.
- Long-term efficacy: While some therapies achieve disease remission, the long-term durability of these responses requires further investigation.
The Role of Biologics
Biologics, a class of drugs derived from living organisms, are a cornerstone of autoimmune disease management. These targeted therapies, including TNF-alpha inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors, and anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibodies, effectively suppress specific inflammatory pathways involved in autoimmune disease development. Biologics offer a more targeted approach compared to traditional immunosuppressants and have significantly improved the quality of life for many patients.
Conclusion
The field of immunotherapy for autoimmune diseases is rapidly advancing, offering promising avenues for more specific and effective treatments. Although challenges persist, ongoing research in novel targets, personalized approaches, and combination therapies paves the way for a future where the immune system itself can be harnessed to fight these debilitating conditions.
Immunotherapy 2.0: Smarter Use, Better Results: Watch this video