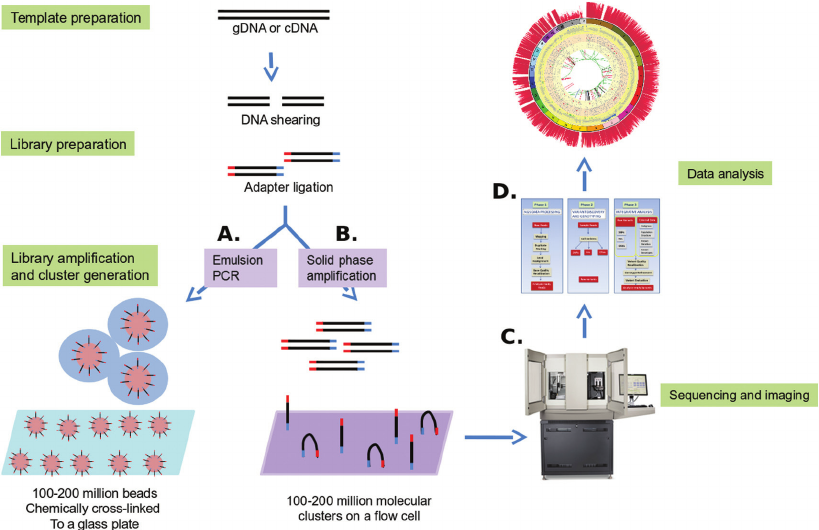
Genetic testing and diagnostics have significantly improved our understanding of disease and hold great promise for personalized medicine. However, this technology raises several ethical issues that scientists and researchers must address.
1. Informed Consent and Autonomy
A core principle is ensuring informed consent before genetic testing. Patients must clearly understand the potential implications of the results, including test limitations, the possibility of unexpected findings, and the psychological impact of positive or negative results. This necessitates qualified professionals providing comprehensive genetic counseling before and after testing.
2. Privacy and Confidentiality
The sensitive nature of genetic information necessitates strict regulations to protect it from unauthorized access, disclosure, or misuse. Whenever possible, researchers must anonymize or pseudonymize data and implement robust data security measures.
3. Genetic Discrimination
The potential for genetic discrimination in employment, insurance, and healthcare access is a major concern. Legislation is crucial to prevent using genetic information for discriminatory purposes, and public education can help dispel myths and promote understanding of genetic testing.
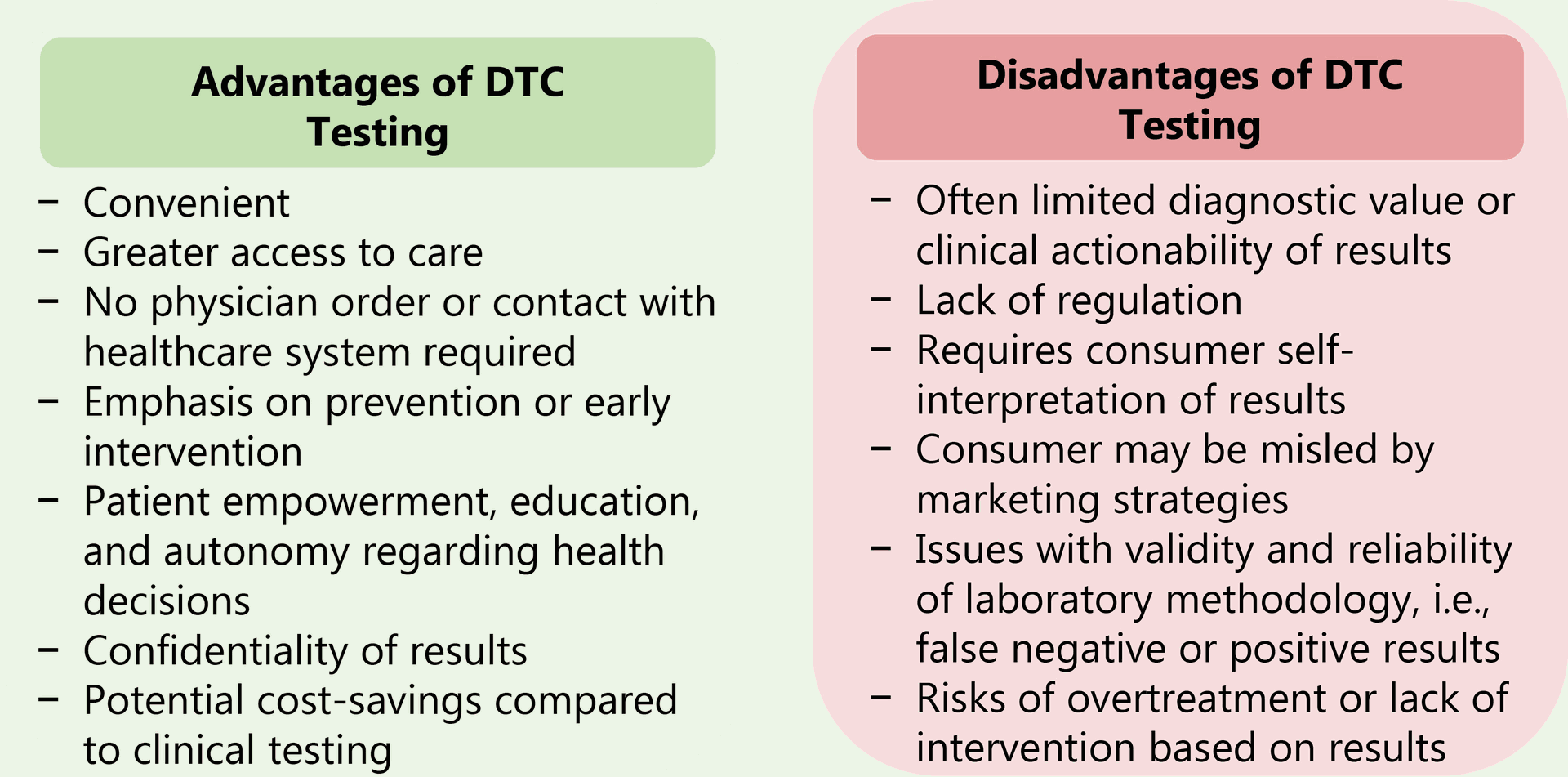
4. Ethical Concerns of Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Testing
The rise of DTC genetic testing kits presents new ethical challenges. These tests may not be as comprehensive or clinically validated as those administered by healthcare professionals, and the quality of genetic counseling from DTC companies can vary. Researchers must advocate for strong regulations and quality control measures for DTC testing to ensure patient safety and well-being.
5. Fairness and Equity in Access
Genetic testing costs can be high, potentially creating disparities in access for people from different socioeconomic backgrounds. This raises concerns about fairness and justice in healthcare. Researchers and policymakers must collaborate to develop strategies ensuring everyone has access to affordable and high-quality genetic testing.
6. Ethical Implications of New Technologies
The field of genetic testing is constantly evolving, with new technologies like whole-genome sequencing emerging rapidly. These advancements require ongoing ethical discussions to address issues like interpreting variants of uncertain significance (VUS) and potential unintended consequences. Researchers must be at the forefront of these discussions to ensure the responsible development and implementation of new technologies.
Conclusion
Genetic testing and diagnostics have immense potential to improve human health, but this power comes with significant ethical responsibilities. By fostering open dialogue and collaboration between scientists, researchers, ethicists, and policymakers, we can ensure this powerful technology benefits everyone.
Learn more about Ethical Considerations of Genetic Testing in this video.