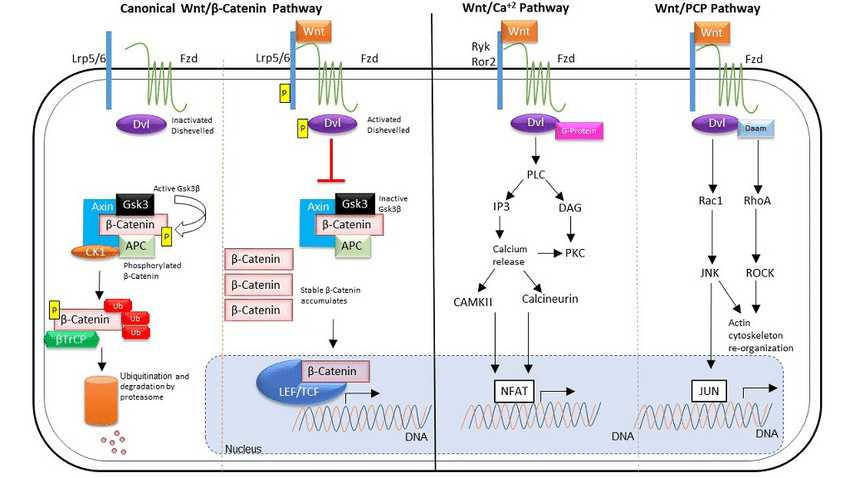
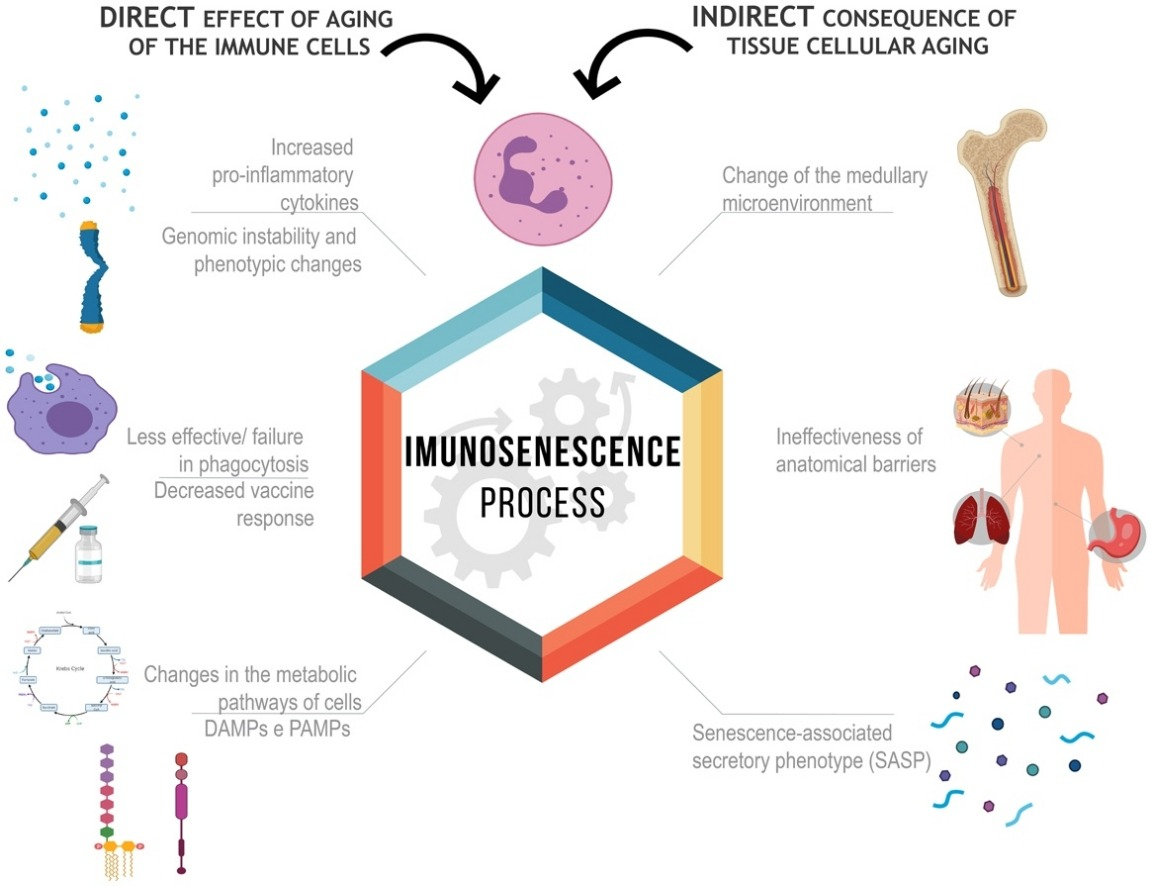
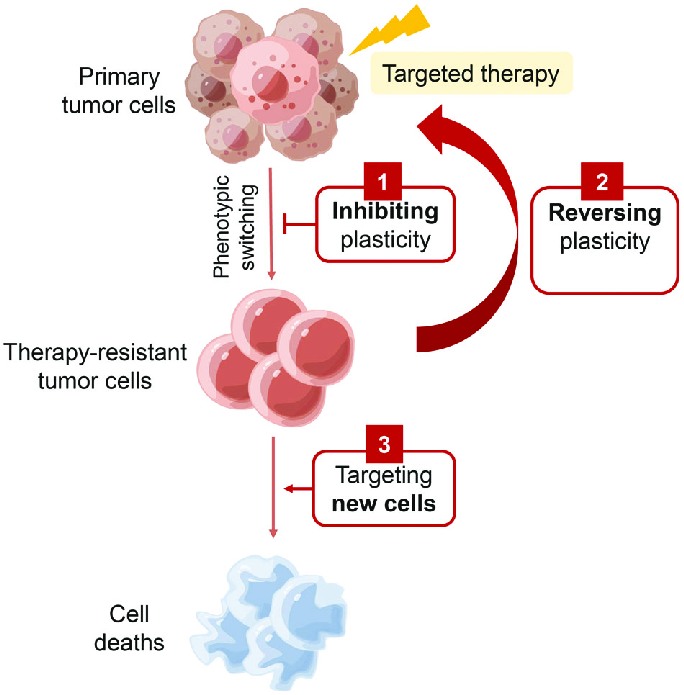
Recent advancements have illuminated previously unknown aspects of cell signaling. Here are some exciting new areas of research:
- Non-canonical signaling: Traditionally, pathways were viewed as linear. However, recent findings reveal intricate interactions and context-dependent variations within pathways. This "non-canonical" signaling adds complexity but also offers promising therapeutic possibilities.
- Spatial dynamics: Signaling molecules not only interact but also exhibit specific locations within the cell. Techniques like optogenetics allow researchers to manipulate the positioning of signaling components, revealing how spatial cues influence cellular decisions.
- The role of non-coding RNAs: Beyond protein-protein interactions, non-coding RNAs like microRNAs are emerging as key regulators of cell signaling. Understanding their influence on pathway activation and regulation holds immense therapeutic potential.
Connecting the Dots: Cell Signaling and Disease
Disruptions in cell signaling pathways are a hallmark of many diseases, including cancer. Here's how these pathways contribute:
- Oncogenic signaling: Mutations in genes encoding signaling proteins can lead to constant activation of pathways that promote uncontrolled cell growth, a defining feature of cancer.
- Tumor suppressors: Certain pathways act as brakes on cell division. Mutations that inactivate these tumor suppressor pathways can contribute to tumor formation.
- Chronic inflammation: Abnormal activation of inflammatory signaling pathways can create a microenvironment that promotes cancer progression.
These insights have led to the development of targeted therapies that modulate specific signaling pathways.
Targeting the Cellular Communication System: Therapeutic Interventions
The knowledge gained from studying cell signaling pathways is being translated into novel therapeutic strategies:
- Small molecule inhibitors: These drugs target specific proteins within pathways, blocking their activity and disrupting oncogenic signaling.
- Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs): ADCs combine the targeting ability of antibodies with the cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic drugs, delivering potent therapy directly to cells with altered signaling pathways.
- Immunotherapy: By manipulating immune checkpoints, some immunotherapies harness the body's own immune system to target cells with aberrant signaling.
Maxanim, a trusted supplier of research reagents, offers a comprehensive portfolio of tools to study cell signaling pathways. Their high-quality antibodies, proteins, and inhibitors can aid researchers in dissecting the complexities of these pathways and furthering our understanding of human health and disease.
Future Directions: Continued Exploration of Cellular Communication
The exploration of cell signaling pathways is an ongoing endeavor. Deciphering novel mechanisms, dissecting the role of spatial dynamics, and harnessing the power of non-coding RNAs will be at the forefront of future research. By continuing to investigate these pathways, we can unlock new avenues for treating diseases and improving human health.
Learn more about Common cell signaling pathway in this video: