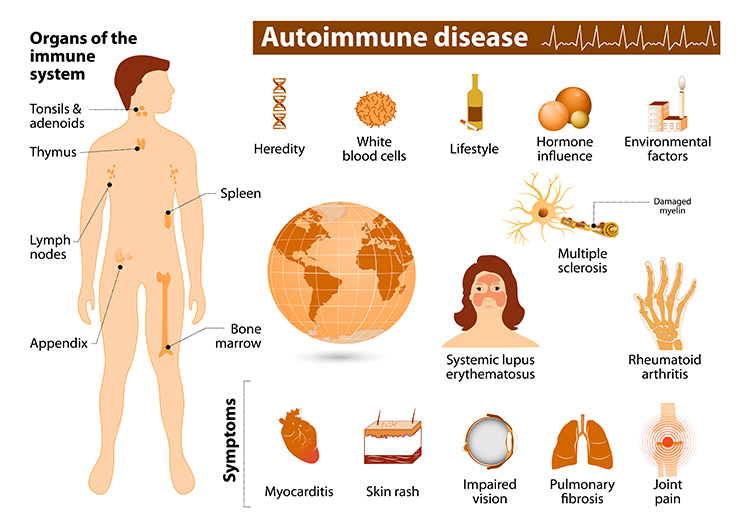
Autoimmune diseases are a group of conditions where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues. This can lead to a wide range of symptoms depending on the affected organ or tissue. Examples include rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Researchers are working to understand the exact causes of autoimmune diseases and develop new treatments.
Causes of Autoimmune Diseases
Several factors can contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases:
- Genetics: Certain genes make people more susceptible to autoimmune diseases.
- Loss of immune tolerance: Normally, the immune system learns to distinguish between "self" and "non-self" molecules. In autoimmune diseases, this tolerance is lost, leading the immune system to attack the body's own tissues.
- Molecular mimicry: Sometimes, foreign molecules from viruses or bacteria closely resemble the body's own molecules. This can confuse the immune system and trigger an attack on healthy tissues.
Current and Emerging Treatments for Autoimmune Diseases
There is no cure for most autoimmune diseases, but treatments can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression. Current therapies focus on suppressing the overactive immune response. These include:
- Immunosuppressant medications: These drugs weaken the immune system overall.
- Targeted immunomodulatory therapies: These newer drugs target specific molecules or pathways involved in the immune response, offering a more precise approach. Companies like Maxanim provide research reagents that aid in the development of these targeted treatments.
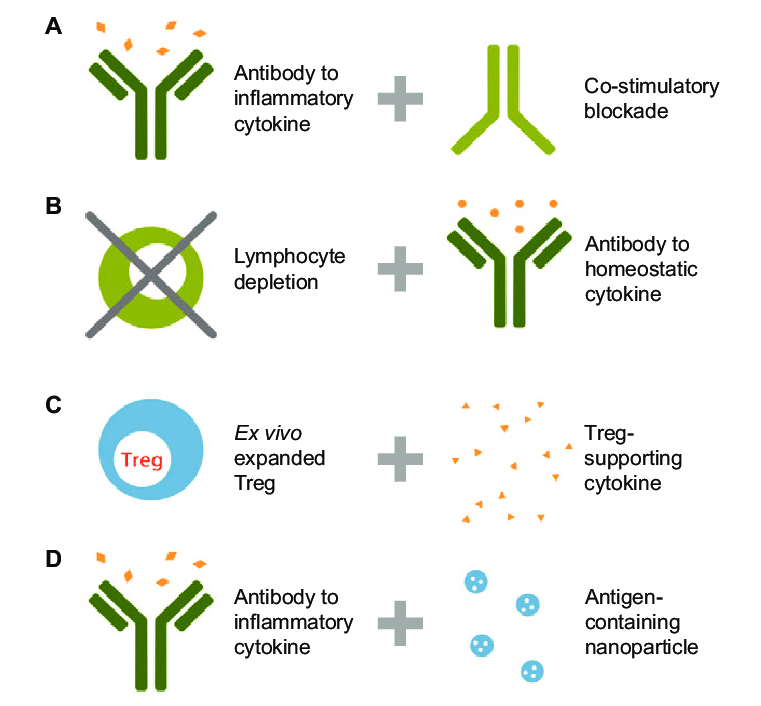
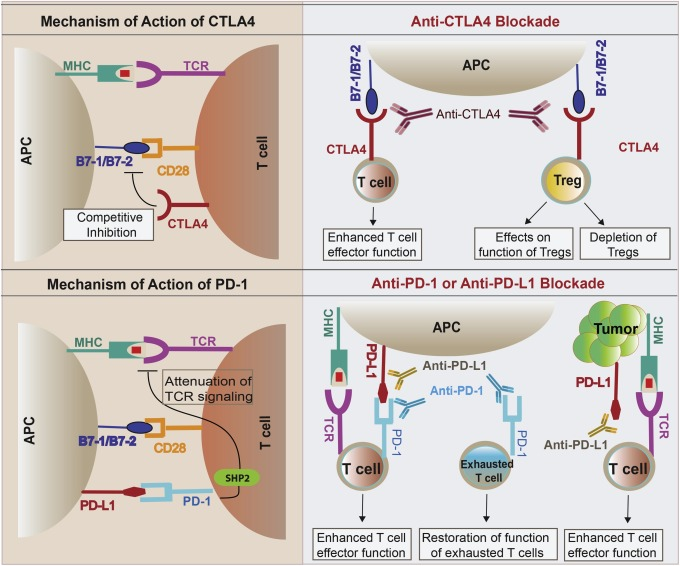
Researchers are also exploring promising new avenues for treatment:
- Immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors: These therapies, already successful in cancer treatment, are being investigated for autoimmune diseases. They work by boosting the activity of regulatory T cells, which help keep the immune system in check.
- Microbiome-based therapies: The gut microbiome, the community of microbes living in the intestines, plays a role in immune function. Studies suggest that imbalances in the gut microbiome may be linked to autoimmune diseases. Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) and manipulating gut bacteria composition are being explored as potential therapeutic strategies.
Read more about The Future of Microbiome Therapeutics below.
Future Directions
Autoimmune diseases are complex conditions, but ongoing research offers hope for improved treatments and potentially even prevention strategies. Understanding the role of genetics, immune tolerance, and the gut microbiome will be crucial for future breakthroughs.